RT-qPCR services
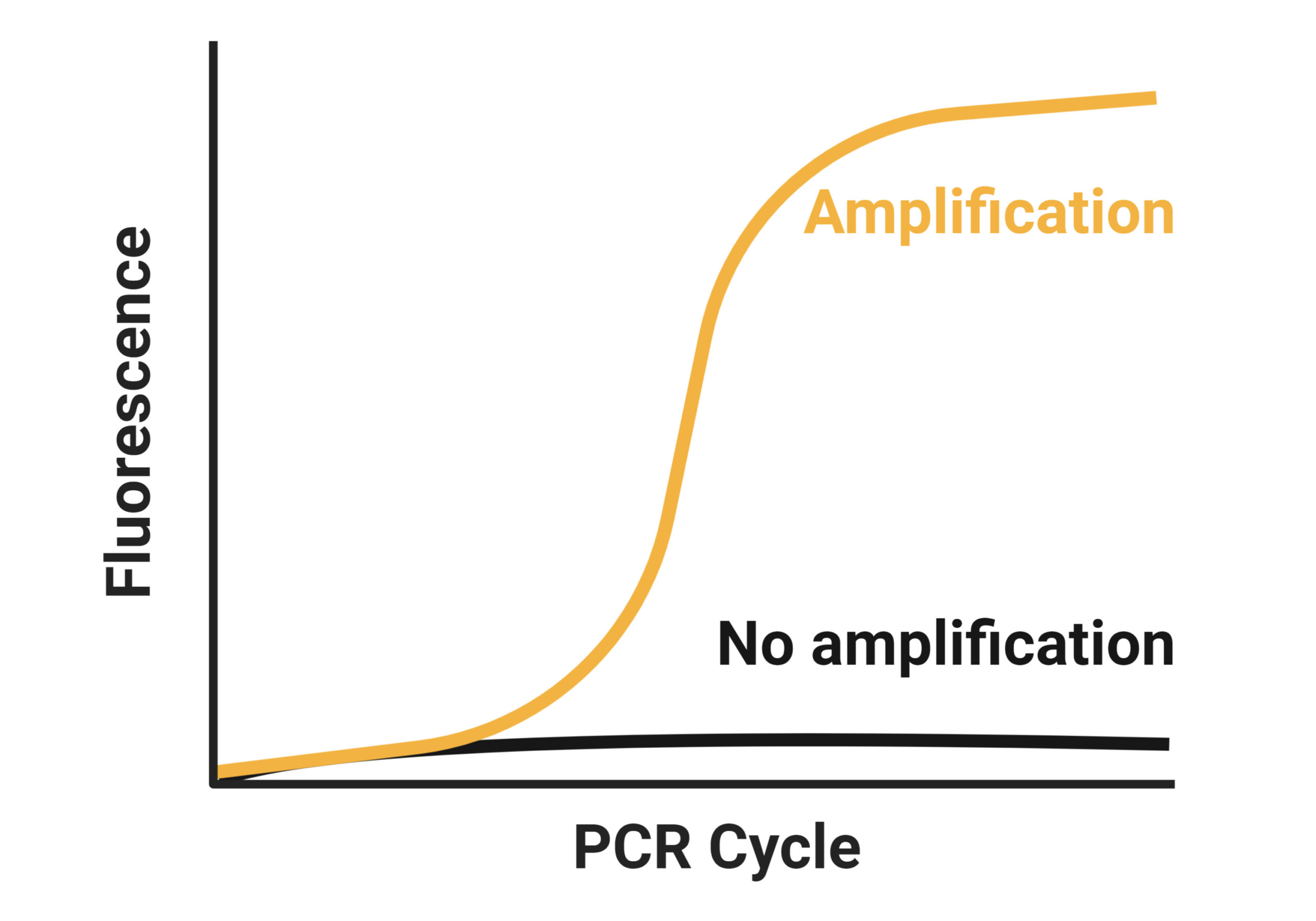
Reverse-transcription quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) is ideal for a sensitive and specific gene expression analysis including microRNAs, other small and large non-coding RNAs, as well as messenger RNA.
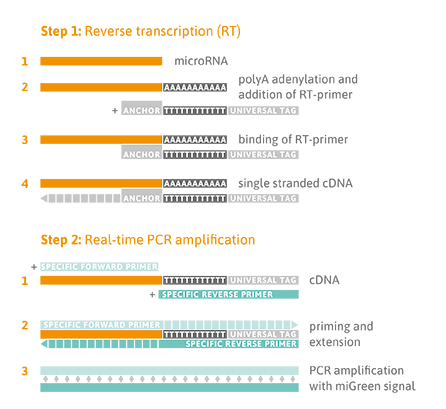
TAmiRNA is an expert in developing and applying RT-qPCR assays for various RNA types. Our microRNA platform takes advantage of target-specific LNA-enhanced (locked nucleic acid) forward and reverse primers with unmet specificity and sensitivity. We use this assay for parallel quantification of 1 up to 768 microRNAs per cDNA sample. The high sensitivity allows us to analyze low RNA input samples such as biofluids, cell culture supernatants, extracellular vesicles (EVs), and microdissected tissues without pre-amplification.
benefits
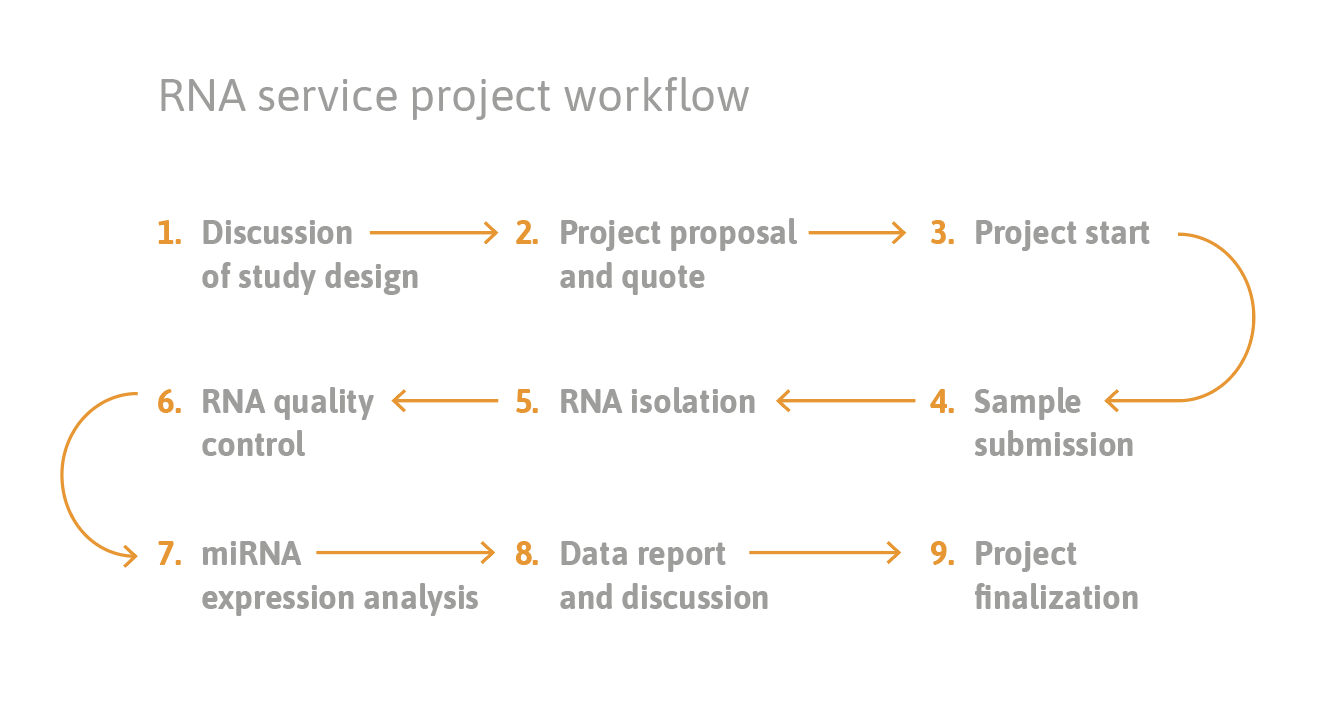
What we offer: our one-stop-shop service for microRNA, other non-coding RNA, and mRNA analysis includes RNA extraction, RT-qPCR, data analysis, and reporting of ready-to-publish results. We perform analytical assay validations according to regulatory recommendations.
Target flexibility: Our RT-qPCR services are available for microRNAs, other small and large non-coding RNAs as well as messenger RNAs.
Our promise: RT-qPCR services by TAmiRNA can be included in basic, translational, and pre-clinical research studies as well as clinical trials.
Our experience: RT-qPCR analysis can be performed on cells, tissues, tissue compartments, extracellular vesicles (EVs) and exosomes, and biofluids from a long list of organisms, including human, non-human primates, mice, rats, pigs, cows, horses, dogs, Chinese hamster (CHO), as well as C. elegans and drosophila.
Your flexibility: we develop customer-tailored assays, perform analytical validation, and transfer validated assays to our customers.
sample requirements
- Biofluids: serum, plasma, urine, CSF, synovial fluid, milk, or cell culture supernatant.
- Extracellular vesicles (EVs): we can isolate EVs in-house or work with material provided by our customers.
- Cells and tissues: how low can we go? very low – 10,000 µm2 dissected tissue area or ~ 100 cells
service description
- Total RNA extraction from various biological matrices.
- RT-qPCR analysis of microRNAs, small and large non-coding RNAs, and messenger RNAs.
- Data analysis, reporting, and interpretation support.
- Customer-tailored assay development.
- Analytical validation.
- Assay Transfer.
reference projects
Circulating endothelial extracellular vesicle signatures correspond with ICU requirement: an exploratory study in COVID-19 patients. Zipperle J, Oesterreicher J, Hackl M et al. Intensive Care Med Exp. 2023 Nov 30;11(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s40635-023-00567-7
Circulating microRNAs in young individuals with long-duration type 1 diabetes in comparison with healthy controls. Swolin-Eide D, Forsander G, Pundziute Lyckå A et al. Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 19;13(1):11634. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-38615-7.
Identification of circulating microRNA patterns in patients in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis Haschka J, Simon D, Bayat S et al. Rheumatology, 2023 Feb 3, https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kead059
MicroRNA profiling reveals distinct signatures in degenerative rotator cuff pathologies. Plachel F, Heuberer P, Gehwolf R et al. J Orthop Res. 2019 Sep 14. doi: 10.1002/jor.24473
MicroRNAs in porcine uterus and serum are affected by zearalenone and represent a new target for mycotoxin biomarker discovery. Grenier B, Hackl M, Skalicky S et al. Sci Rep. 2019 Jun 28;9(1):9408. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-45784-x
Biotransformation of the Mycotoxin Zearalenone to its Metabolites Hydrolyzed Zearalenone (HZEN) and Decarboxylated Hydrolyzed Zearalenone (DHZEN) Diminishes its Estrogenicity In Vitro and In Vivo. Fruhauf S, Novak B, Nagl V et al. Toxins (Basel). 2019 Aug 20;11(8). pii: E481. doi: 10.3390/toxins11080481
SVF-derived extracellular vesicles carry characteristic miRNAs in lipedema. Priglinger E, Strohmeier K, Weigl M et al. Sci Rep. 2020 Apr 29;10(1):7211. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-64215-
Unique, Gender-Dependent Serum microRNA Profile in PLS3 Gene-Related Osteoporosis Mäkitie RE., Hackl M., Weigl M et al. J Bone Miner Res. 2020 May 26. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.4097.
MicroRNA Expression Profile Changes after Cardiopulmonary Bypass and Ischemia/Reperfusion-Injury in a Porcine Model of Cardioplegic Arrest Kiss A., Heber S., Kramer A-M et al. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 240; doi:10.3390/diagnostics10040240.
MicroRNA levels in bone and blood change during bisphosphonate and teriparatide therapy in an animal model of postmenopausal osteoporosis Kocijan R, Weigl M, Skalicky S et al. Bone 2019 Nov 1:115104. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2019.115104.
Combining laser microdissection and microRNA expression profiling to unmask microRNA signatures in complex tissues Skalicky S, Zwiers PJ, Kuiper T et al. Biotechniques. 2019 Oct 17. doi: 10.2144/btn-2019-0032. Epub 2019 Oct 17